
A barcode is a uniquely encoded image that makes it possible for computer systems to scan and identify physical objects. There are around 30 different major barcode formats, which typically fall into two categories: 1-dimensional (1D) or 2-dimension (2D).
This handy blog will guide you through the most used barcodes, why you should use them and how to implement a barcode tracking system in minutes using your smartphone 👇
Types of Barcodes: 1D Barcodes (Linear Barcodes)
A 1D barcode is a horizontal image made up of black and white lines, in different widths and spaces, used to encode information.
There are a variety of advantages to using 1D barcodes, including:
📈 Simple & cost-effective to create
📦 The universal compatibility means that several industries can implement these barcodes across products, including UPC, EAN and Code 128
🖨️ Easy to create and download, and scan with computer devices and scanners
🔢 The lightweight data storage (max. 25 characters) makes it easy for products or applications with simple numeric or alphanumeric information to use
Most Common 1D Barcode Types
UPC (Universal Product Code)
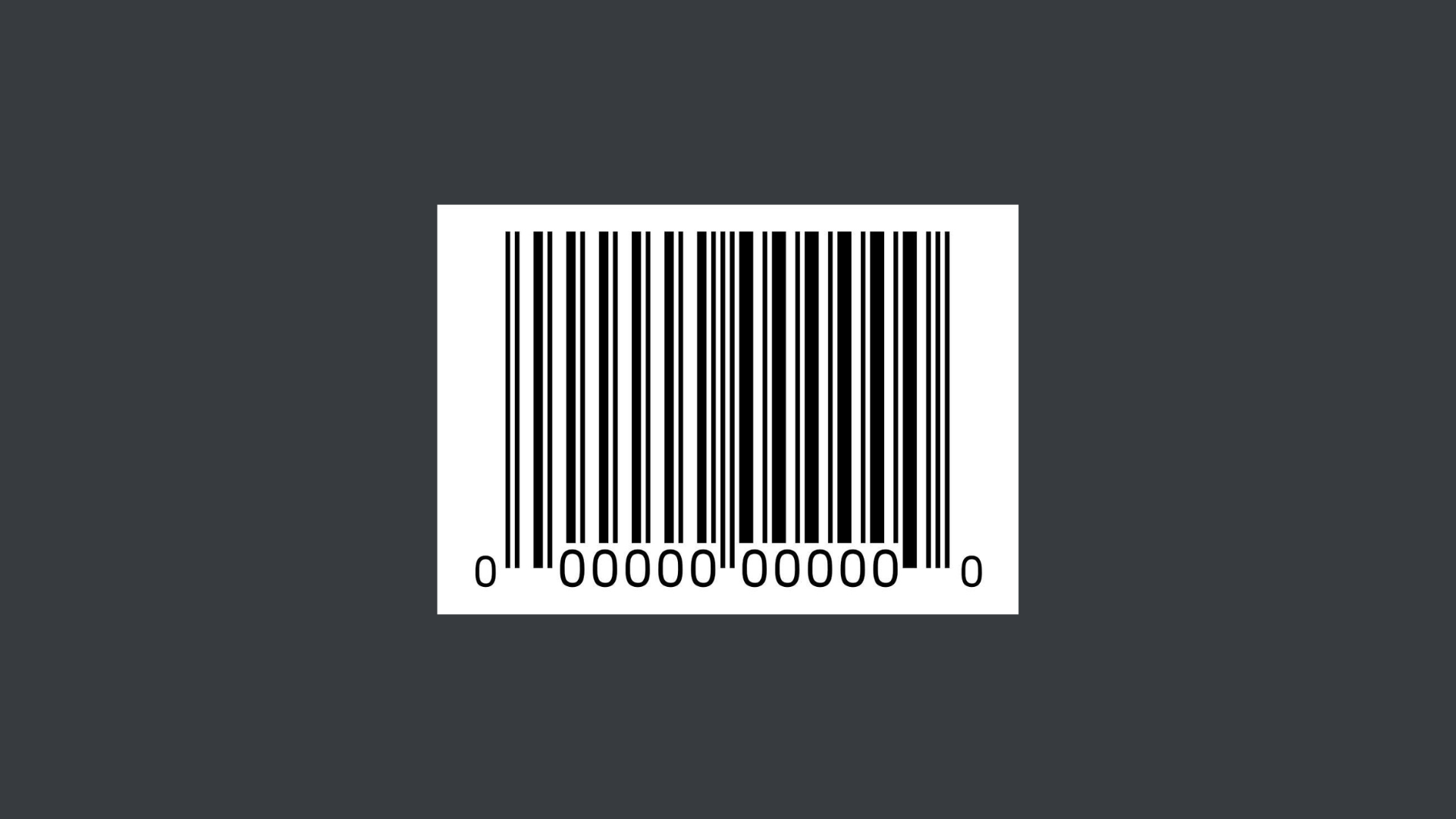
UPC barcodes are used globally for retail point-of-sale products to allow POS systems to read and register the product, description and sale price. UPCs can be displayed in 2 formats:
EAN (European Article Number)

EAN barcodes are widely used around the world for retail point of sale applications. The most common format is EAN-13 which consists of 13 digits, similar to a UPC-A barcode, but includes a country code which makes it suitable for international use.
Whilst, EAN-8: consists of 8 digits for smaller packages.
Code 128

Widely used in logistics, shipping and packaging due to its ability to encode large amounts of data in a small space. The Code 128 barcode can hold high density, alphanumeric data. The GS1-128 variant includes application identifiers like expiry dates, batch numbers and weights.
Code 39
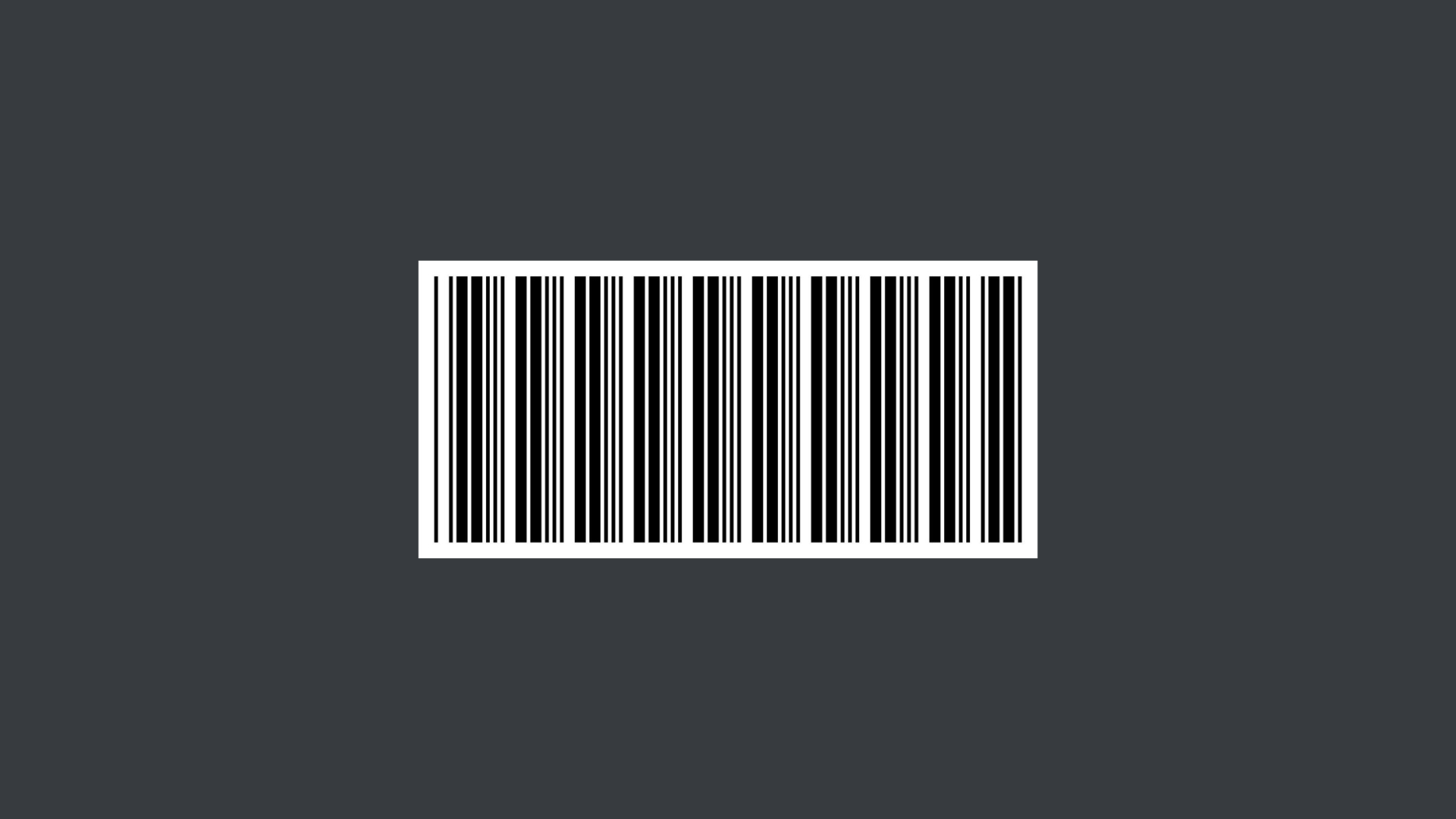
Code 39 is an alphanumeric barcode used in the automotive, manufacturing and healthcare industries to support tracking parts and the inventory of parts, deliveries, staff and more, as well as medical records. It can encode letters and numbers without the need for complex coding.
It is limited by its size, as Code 39 barcodes require more space than others.
Less Common 1D Barcodes Types
ITF (Interleaved 2 of 5)

A number only barcode, made up of pairs of digits which makes it a compact and efficient barcode used for a high volume of scanning. Therefore, it is widely used for packaging materials like corrugated boxes. What makes this barcode different is that it is printed directly onto rough materials, not as an attached label.
A key variant of this is the ITF-14, which is used for barcode labels in the supply chain, particularly for shipping containers, and includes a 14-digit Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) for product identification.
Code 93
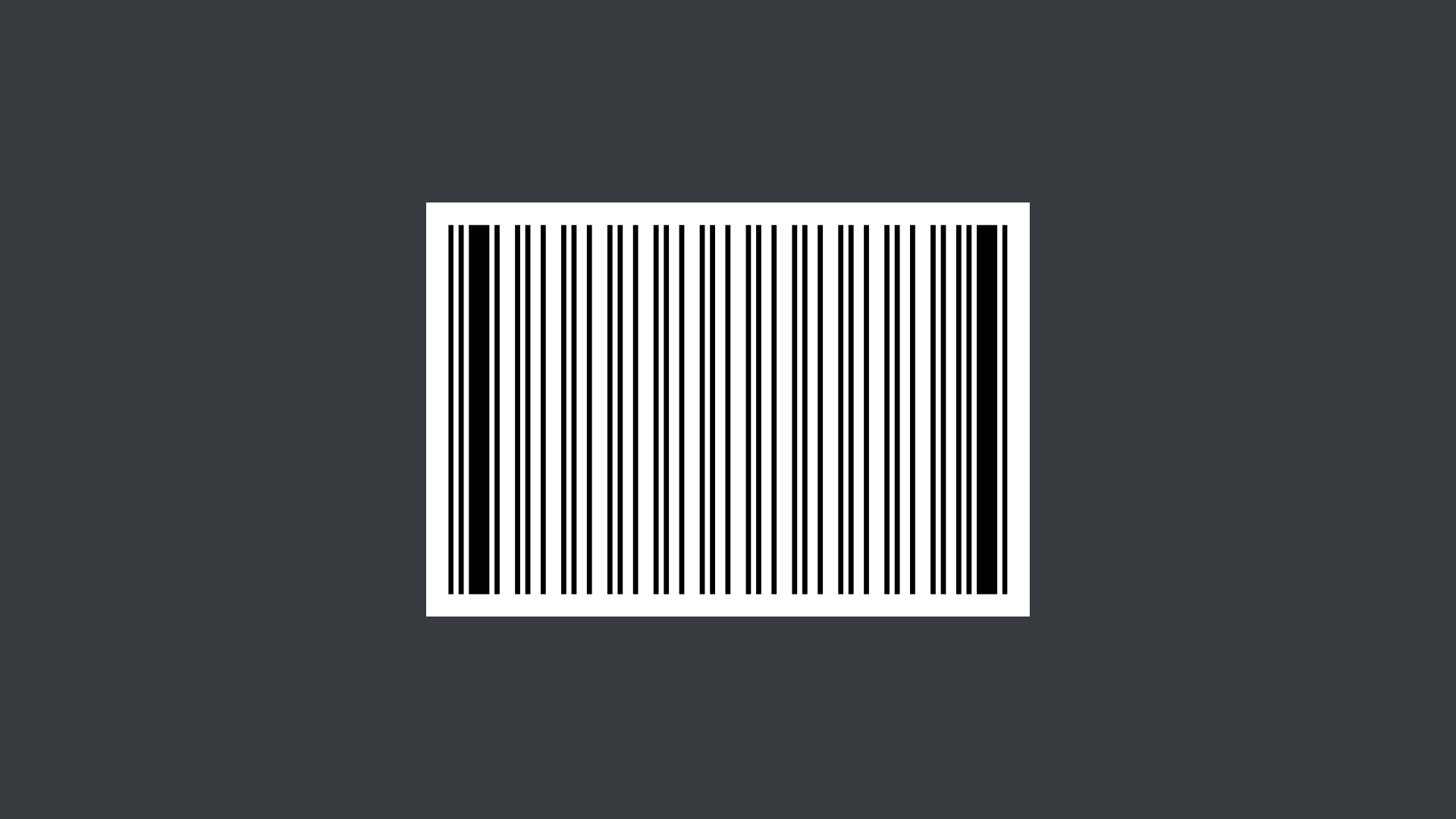
Similar to Code 39, these barcodes are more efficient as they hold alphanumeric data, including numbers, letters, and special characters. Similar to Code 39, but more compact and efficient because they can encode more data in a smaller space. Code 93 is often used in industries where space is limited, such as the Canada Postal service.
Types of Barcodes: 2D Barcodes (Matrix Codes) 🔲
2D barcodes are either square or rectangular shaped, and contain many small, individual dots.
There are many benefits to using 2D barcodes, but most importantly these barcodes…
📈 Hold almost 100% more data than 1D barcodes
⏳ Easy to create and generate so require less time and costs
📲 Can be read using any smartphone, tablet or scanner
The Most Common 2D Barcode Types?
QR Code
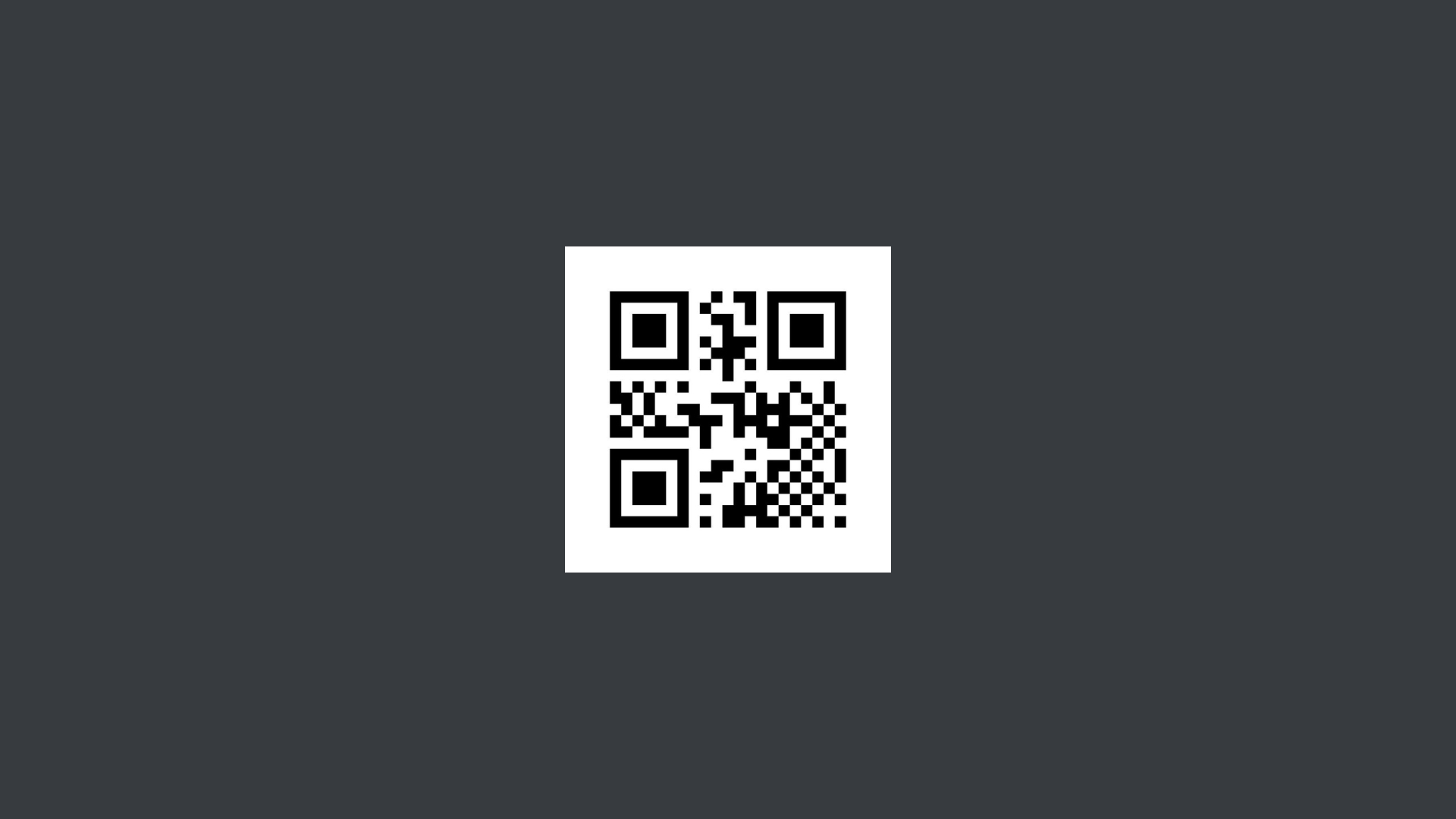

QR codes are becoming more and more popular in marketing and advertising as they give the option for further engagement by providing links to websites, social media, contact information and more. Their use in retail is also increasing, especially through the introduction of GS1 Digital Link and the new dynamic QR codes powered by GS1.
DataMatrix
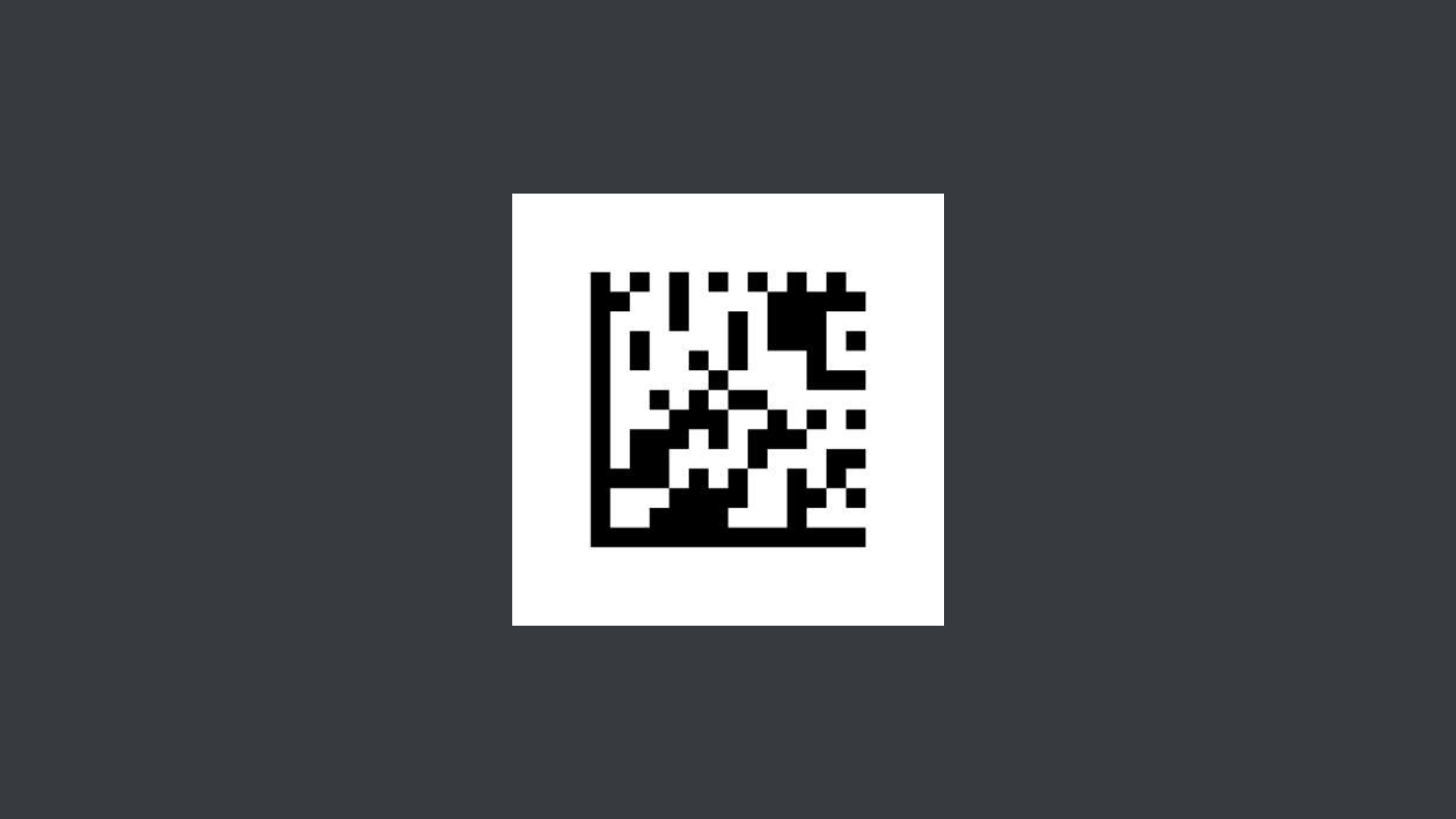

Used in a variety of industries from manufacturing and logistics to the healthcare sector. DataMatrix barcodes are popular due to their small size, but large data density. You’ll see the GS1 variant used in supply chains for tracking and product authentication.
PDF417
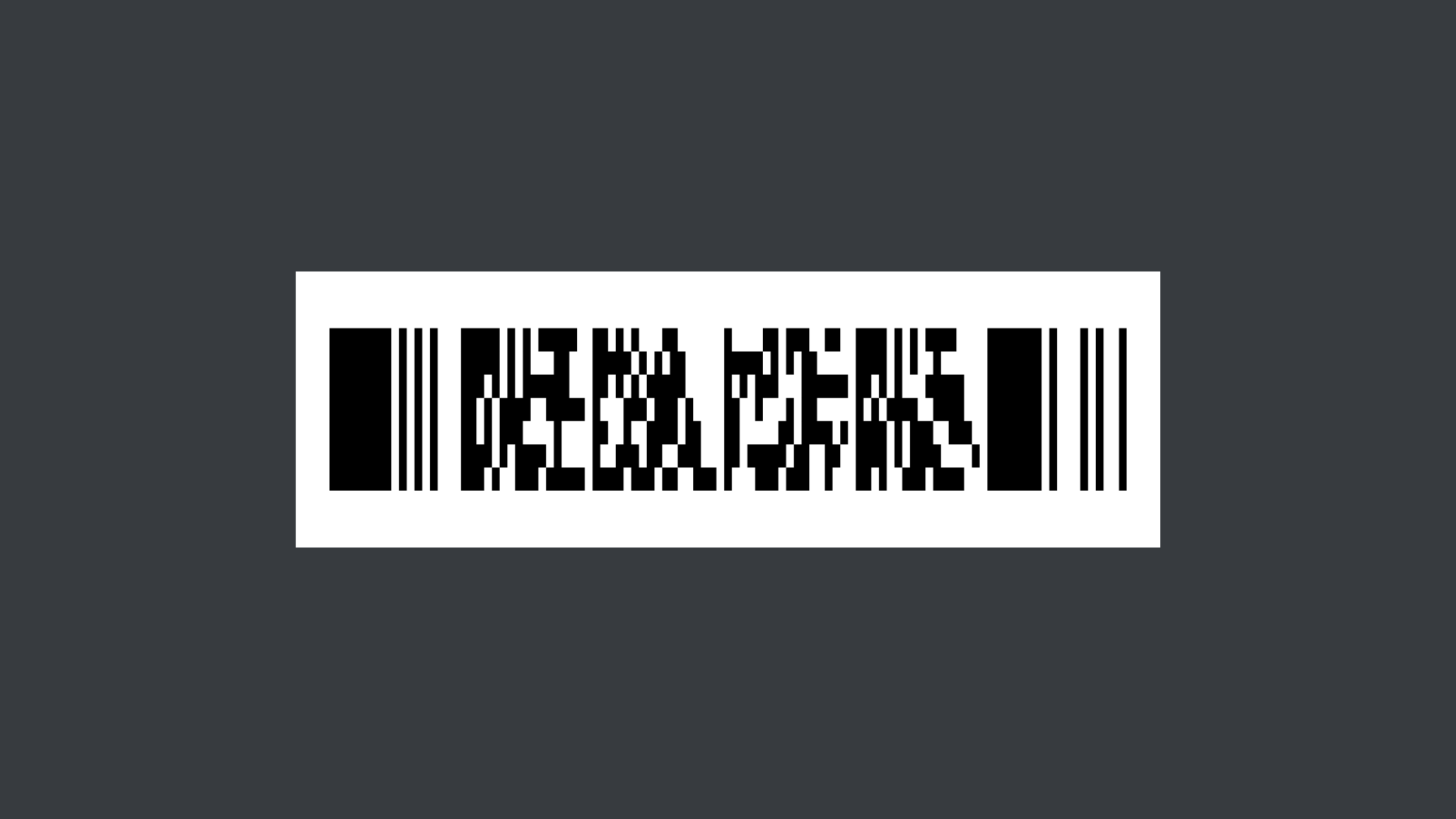

These barcodes are mostly used in the transportation industry due to their high data capacity, covering driver’s licenses, boarding passes and other documentation that identifies personal data.
Aztec Code
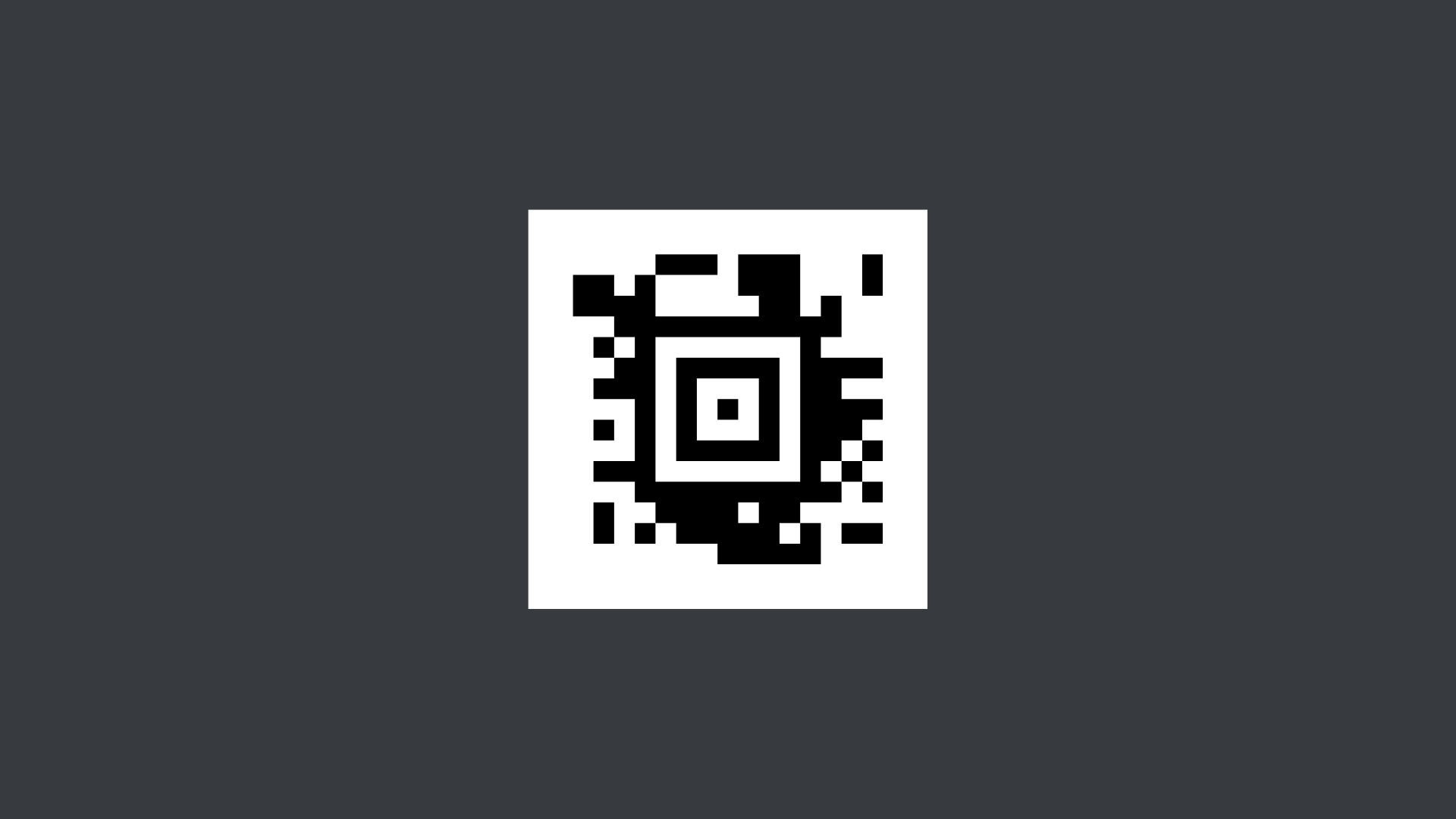

Used in transportation for boarding passes and train tickets as their compact design and high error correction feature makes it easy to scan low quality prints or tickets on mobile phones.
How to choose the right barcode for you? 🎯
When choosing a barcode type, it is important to consider these questions:
- How much data capacity do you require?
- Will the barcode likely be scanned indoors, outdoors, or under harsh conditions?
- What print size do I need?
- Have I checked the industry regulations and label standards?
- Will the chosen barcode integrate with the existing systems?
Top tip: When printing use high quality materials; make sure barcodes are placed correctly on the product and are large enough to be scanned. Always test before batch printing.
Implementing a barcode system with Orca Scan ⚙️
Orca Scan is a GS1 UK-approved barcode tracking app that can be installed on any Apple or Android device, including DataLogic, Honeywell and Zebra barcode scanners.
Use Orca Scan to scan barcodes, and extract all data into the relevant fields in your sheet and roll out a solution in minutes 👏 Plus, it’s a fully customisable system which means you can add additional fields that will capture more information with every scan.
To top it off?
You can now use our brand new Barcode Label Designer to create custom product labels that meet your requirements; choose your ideal barcode, logo, colours and get data directly from your sheets.
Ready to explore all our barcode scanning solutions? 👇
Download the free Orca Scan app today and get scanning! Or if you need help understanding which barcode is right for you? Get in touch with one of our team or book a demo, and we’ll be happy to help 😊
Frequently Asked Barcode Questions:
What are the two main types of barcodes?
Linear (1D) and matrix (2D) barcodes. Linear barcodes represent data as parallel lines, while matrix barcodes use grids to store data.
What is the difference between ITF and UPC?
ITF (Interleaved Two of Five) is used primarily for packaging, whereas UPC is used for retail product identification.
What is the most popular barcode format?
Although UPC is widely used in North America for retail, EAN barcodes are popular globally. But the choice depends on the regional standards you’re in.
What are the different types of scanning codes?
Scanning codes include 1D barcodes such as UPC, EAN, Code 39, and Code 128, and 2D barcodes such as QR codes and Data Matrix which store more data in a compact space.
What is the difference between UPC and barcode?
A barcode is a set of data that is readable by machines and computers, whereas a UPC is a specific type of barcode that encodes a 12-digit number that identifies a product.
What type of barcode do retail stores use?
Retail stores commonly use UPC-A, UPC-E and EAN-13 barcodes for product labelling. QR codes are being used more frequently for inventory tracking, and the new QR Codes powered by GS1 are being used more to increase mobile engagement with customers.
