Validate barcode scan data on your server before it saves. When a user scans a barcode or edits a field in the Orca Scan mobile app, an HTTP POST request sends the captured data to your webhook endpoint. Your server can then verify, reject, or modify the data and return in-app error messages or notifications to guide the user - before anything is saved.
How does the Validation URL work?
- A user scans a barcode or edits a field in the Orca Scan mobile app
- The full data is sent to your Validation URL via HTTP POST
- Your server inspects the incoming data
- You return a response to either:
- allow the data to be saved
- modify the data before saving
- block the save with an error
- Orca Scan applies the response and updates the user interface
Note: Your endpoint must respond within 750ms or the result is ignored.
How do I add a Validation URL to my sheet?
- Log in to the Orca Scan web app
- Select the sheet you want to validate
- Click Integrations in the toolbar
- Click Events API and enter your Validation URL
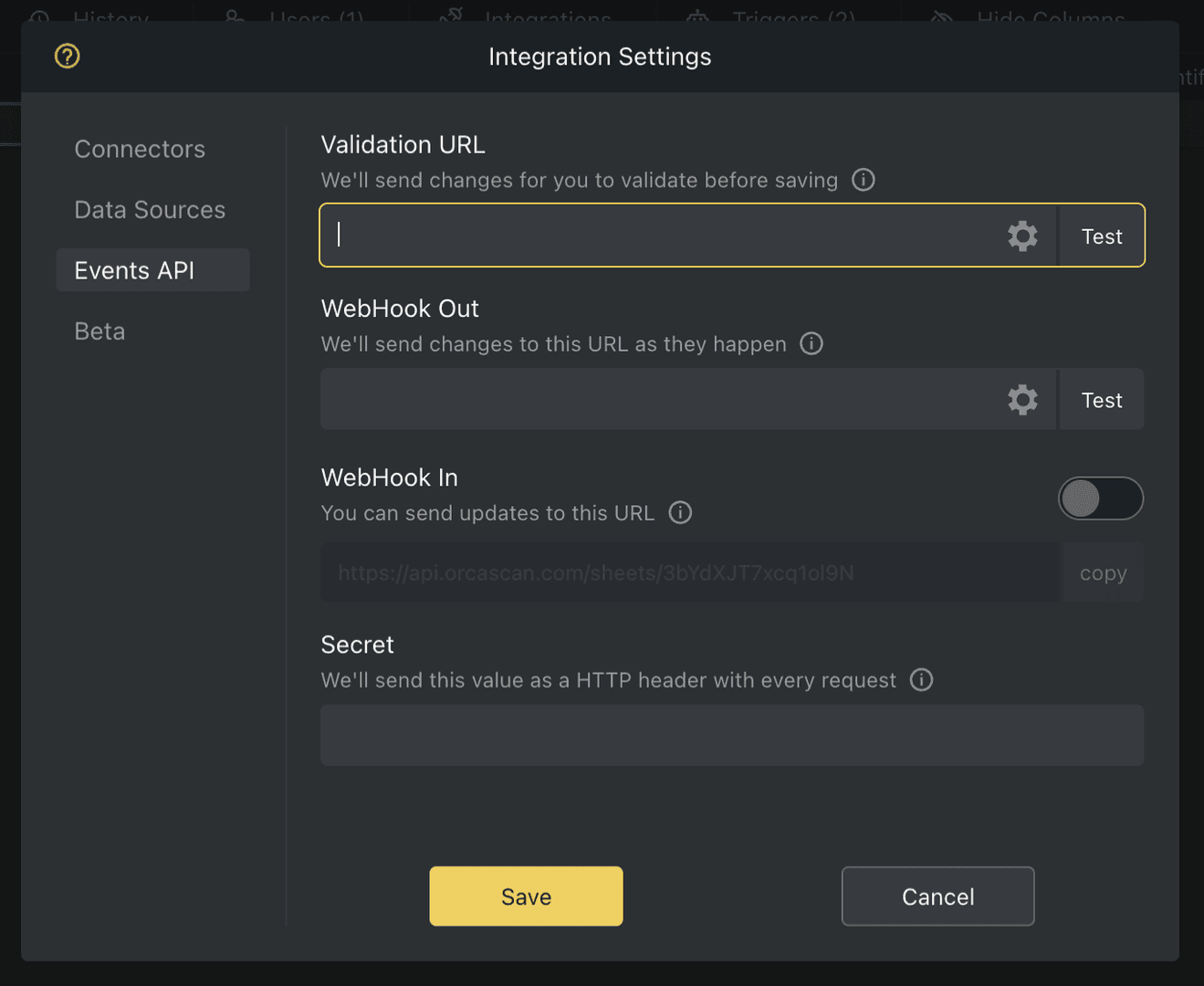
- Click Test to confirm your Validation URL is accessible
- Save the changes
That’s it. Now scan a barcode → enter some data → tap save to validate.
How do I create a Validation URL?
You can create a Validation URL using a few lines of code:
const app = express();
app.use(express.json());
app.post('/', function(request, response){
data = request.body;
// dubug purpose: show in console raw data received
console.log("Request received: \n"+JSON.stringify(data, null, 2));
// orca system fields start with ___
// access the value of fields using field name
// example: data.Name, data.Barcode, data.Location
const name = data.Name
// validation example
if (name.length > 20) {
// return error message to show user
response.json({
"title": "Invalid Name",
"message": "Name cannot contain more than 20 characters",
}).send();
return;
}
// return HTTP Status 204 (no content)
response.status(204).send();
});
app.listen(3000, () => console.log('Example app is listening on port 3000.'));
[ApiController]
[Route("/")]
public class OrcaValidationDotNet : ControllerBase
{
[HttpPost]
[Consumes("application/json")]
public async Task<ActionResult> validationReceiver()
{
using (StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(Request.Body, Encoding.UTF8))
{
// get the raw JSON string
string json = await reader.ReadToEndAsync();
// convert into .net object
dynamic data = JObject.Parse(json);
// orca system fields start with ___
// access the value of fields using field name
// example: data.Name, data.Barcode, data.Location
string name = (data.Name != null) ? (string) data.Name : "";
// validation example
if (name.Length > 20) {
// return error message to show user
return Ok(new {
title = "Name is too long",
message = "Name cannot contain more than 20 characters"
});
}
}
// return HTTP Status 204 (no content)
return NoContent();
}
}
func validationHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// Read body
body, err := ioutil.ReadAll(r.Body)
defer r.Body.Close()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
http.Error(w, err.Error(), 500)
return
}
// Parse JSON data
var barcode OrcaBarcode
jsonErr := json.Unmarshal([]byte(body), &barcode)
if jsonErr != nil {
fmt.Println(jsonErr)
http.Error(w, jsonErr.Error(), 500)
return
}
// dubug purpose: show in console raw data received
fmt.Println(barcode)
// orca system fields start with ___
// access the value of fields using field name
// example: data.Name, data.Barcode, data.Location
name := barcode.Name
// validation example
if (len(name) > 20) {
// return error message to show user
w.Write([]byte(`{
"title": "Invalid Name",
"message": "Name must be less than 20 characters"}
`))
return
}
// return HTTP Status 204 (no content)
w.WriteHeader(204)
}
@app.route('/', methods=['POST'])
def orca_validation():
if request.method == 'POST':
data = request.get_json()
# dubug purpose: show in console raw data received
print("Request received: \n"+json.dumps(data, sort_keys=True, indent=4))
# orca system fields start with ___
# access the value of fields using field name
# example: data["Barcode"], data["Location"]
name = data["Name"]
# validation example
if(len(name) > 20):
# return error message to show user
return json.dumps({
"title": "Invalid Name",
"message": "Name cannot contain more than 20 characters",
})
# return HTTP Status 204 (no content)
return '', 204
if (preg_match('/$/', $_SERVER["REQUEST_URI"])) {
if ($_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] === 'POST') {
$data = json_decode(file_get_contents('php://input'), true);
// orca system fields start with ___
// access the value of fields using field name
// example: data.Name, data.Barcode, data.Location
$name = $data["Name"];
// validation example
if (strlen($name) < 20) {
// return error message to show user
echo json_encode(array(
"title" => "Invalid Name",
"message" => "Name cannot contain more than 20 characters"
));
exit;
}
// return HTTP Status 204 (No Content)
http_response_code(204);
exit;
}
}
@RequestMapping(
value = "/",
method = RequestMethod.POST)
String index(@RequestBody Map<String, Object> data) throws Exception {
// dubug purpose: show in console raw data received
System.out.println(data);
// orca system fields start with ___
// access the value of fields using field name
// example: data.get("Barcode"), data.get("Location")
String name = data.get("Name").toString();
// validation example
if (name.length() > 20) {
// return error message to show user
JSONObject json = new JSONObject();
json.put("title", "Invalid Name");
json.put("message", "Name cannot contain more than 20 characters");
return json.toJSONString();
}
// return HTTP Status 204 (no content)
return "";
}
Full working examples for each language are available on GitHub.
HTTP Headers
Each Validation request includes HTTP headers that identify the source sheet, the user who triggered the barcode scan, and the request type. Use these headers to verify the request, apply sheet specific logic, and log or audit barcode scan activity.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
orca-sheet-id |
Unique ID of the Orca Scan sheet |
orca-sheet-name |
The name of the sheet making the request |
orca-user-email |
Email of user scanning the barcode (requires HTTPS) |
orca-timestamp |
UNIX epoch time of the request |
orca-secret |
Sheet assigned secret (check this to verify request) |
orca-request-type |
validation |
Request Body
On validation, Orca Scan sends a POST request containing the full row data and context about the request (sheet name, user email and unique row id). Below is an example of the payload your validation endpoint will receive:
{
"___orca_sheet_name": "sheet",
"___orca_user_email": "user@email.com",
"___orca_row_id": "69a0196a34cb25512f2f2450",
"Barcode": "Orca Barcode",
"Title": "Orca Scan",
"Column Title": "Row Value"
}
Barcode Scan Validation FAQs
How do I reject invalid data?
Return a HTTP status code 400 to reject data.
How do I show an error dialog in the app?
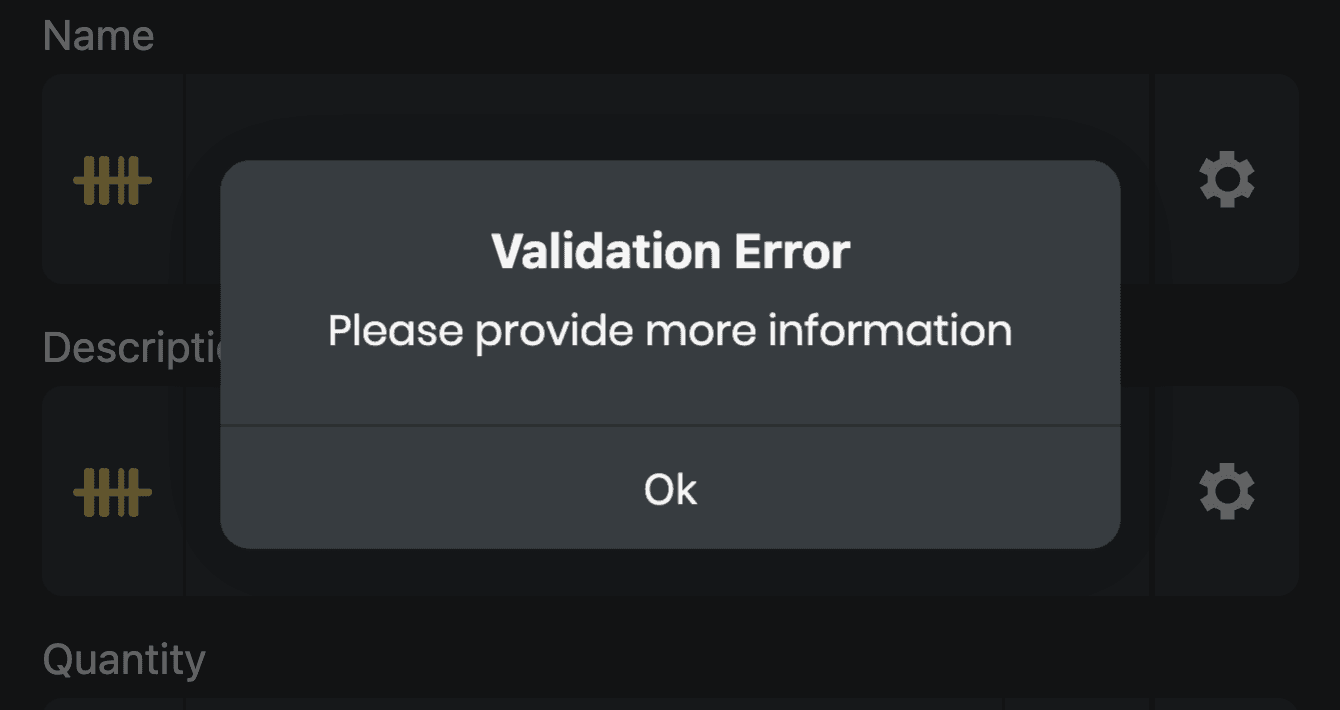
Return a HTTP status code 400 along with an ___orca_message with display set to dialog and type set to error, for example:
{
"___orca_message": {
"display": "dialog",
"type": "error",
"title": "Validation Error",
"message": "Please provide more information"
}
}
A dialog will appear and the user will be unable to proceed until resolved:
How do I show a notification in the app?
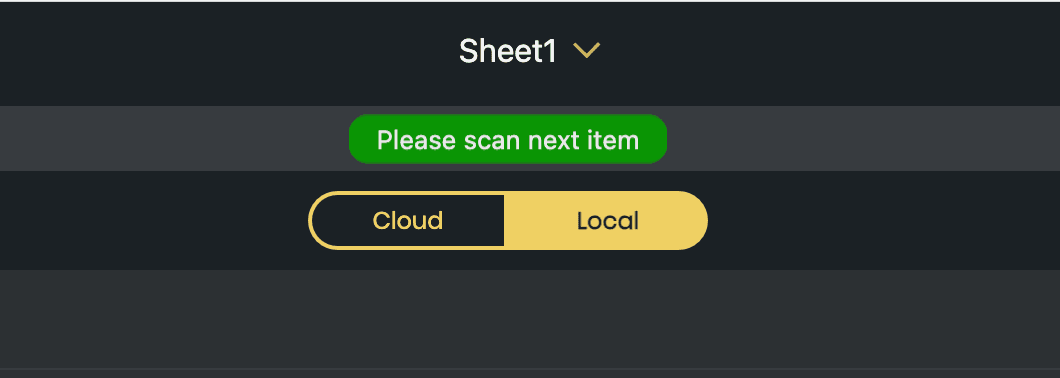
Return an ___orca_message with display set to notification, for example:
{
"___orca_message": {
"display": "notification",
"type": "success",
"message": "Please scan next item"
}
}
A notification will appear briefly at the top of the app:
There are three types of notifications to choose from:
| Type | Appearance |
|---|---|
error |
A red notification appears at the top of the app. |
warning |
A yellow notification appears at the top of the app. |
success |
A green notification appears at the top of the app. |
Can the Validation URL modify the data?
Yes. Simply return a HTTP status code 200 along with the modified data as a JSON object. The Orca barcode app will apply these changes, and, if no ___orca_message is present, allow the user to save:
{
"barcode": "hello@orcascan.com",
"notes": "Not that important :)"
}
How do I connect my development machine?
Expose your local service to the internet so Orca Scan can send Validation requests to it. The easiest way is using localtunnel:
# expose port 3000 to the internet (change if needed)
npx localtunnel --port 3000
Use the temporary HTTPS URL as your Validation URL during development, then replace it with a permanent public URL when deploying.
How do I secure my Validation URL?
Add a secret to your sheet and validate it on every request. The secret is sent as an HTTP header, or can be passed as a query parameter if required.
Need help setting up a Validation URL?
We’re happy to help, chat with us live or book a free implementation call.